Goodbye to the hydraulic Atlas, and hello to the future—Boston Dynamics unveils its electrifying new Atlas, marking a pivotal shift in the robotics landscape.
The transition from a hydraulic powerhouse to a sleek, electric model is not just a change in mechanics; it represents a significant evolution in the field of humanoid robotics. This shift has profound implications for the future of robotics, signaling a move towards more practical, scalable, and commercially viable solutions.
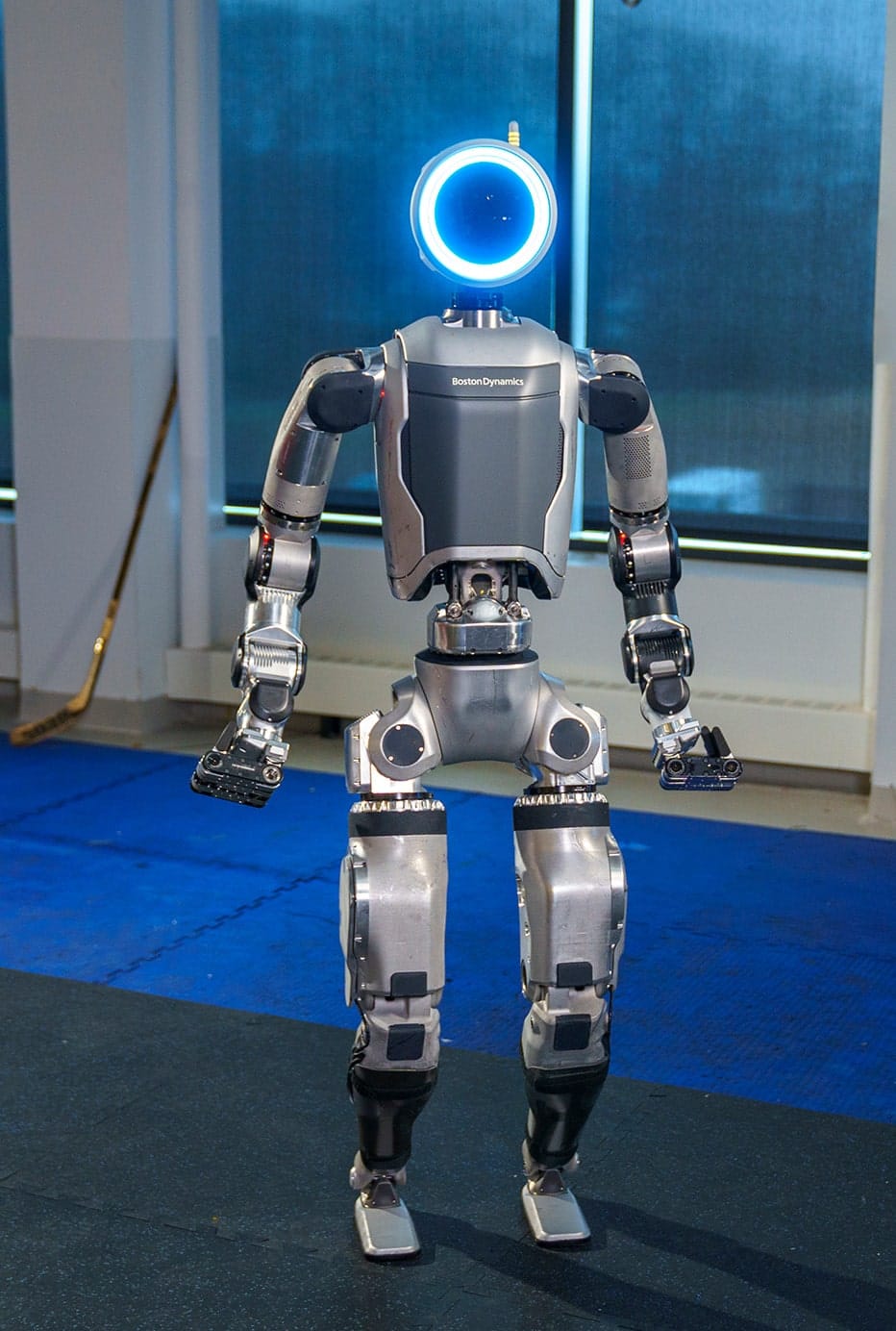
The Legacy of Atlas
The journey of Atlas began with a bold experiment: sawing a pneumatically powered quadruped in half. This initial venture in 2009 marked the birth of Boston Dynamics' humanoid ambitions. The early version of Atlas, known for its tethered, lumbering movements, was a proof of concept that showcased the potential of legged robots.
By 2013, Atlas had evolved significantly. Unveiled to the world as a humanoid capable of walking, the robot was initially designed for disaster response scenarios, demonstrating its ability to traverse rough terrains and navigate obstacles. This version of Atlas laid the groundwork for future iterations by proving that a bipedal robot could maintain balance and perform basic tasks in challenging environments.
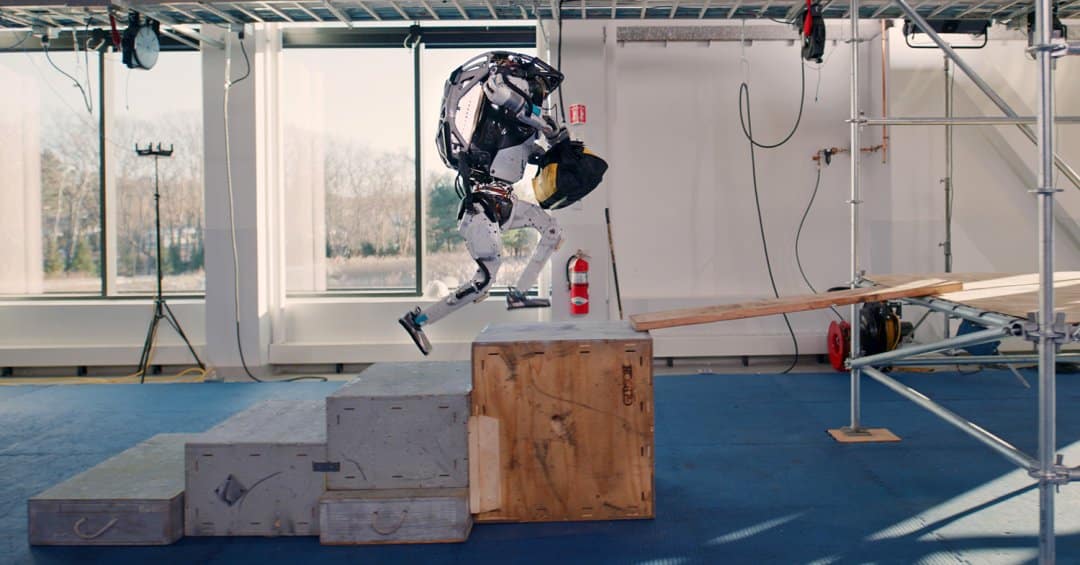

Technological Evolution:
The evolution of Atlas has been marked by continuous improvements in its form factor, sensors, and AI capabilities. The initial bulky design has been streamlined into a more compact and efficient form, allowing for greater mobility and versatility.
Form Factor:
The initial hydraulic model was large and cumbersome. Over time, engineers have reduced its size and weight, making it more agile and suitable for practical applications.
Sensors:
Early models had basic sensors for balance and movement. Modern versions boast a suite of advanced sensors, including LIDAR, stereo vision, and touch sensors, enhancing its ability to perceive and interact with its surroundings.
AI Capabilities:
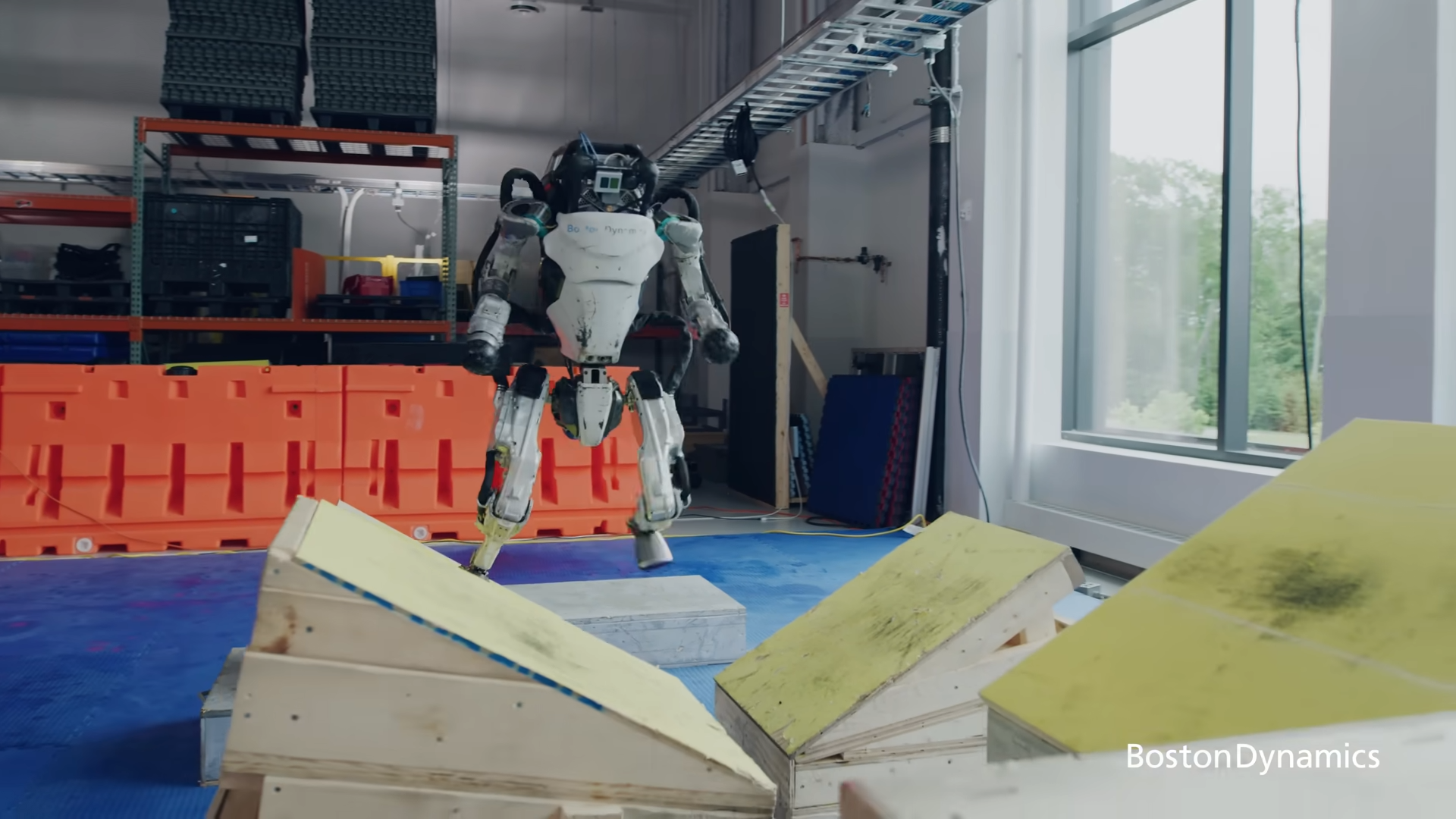
Atlas's AI has evolved from basic movement algorithms to complex decision-making systems. The latest iterations can perform dynamic tasks such as parkour, demonstrating a high level of adaptability and learning.
The continuous evolution of Atlas reflects Boston Dynamics' commitment to advancing the field of robotics. As Atlas transitions to an all-electric model, it carries forward this legacy of innovation, promising even greater advancements in the future.

Technological Advancements in the New Electric Atlas
The decision to transition from hydraulic to electric power in the new Atlas model marks a significant technological shift for Boston Dynamics. Several key factors influenced this move:
- Efficiency: Electric actuators are more efficient than their hydraulic counterparts, reducing energy consumption and increasing overall performance.
- Range of Motion: Electric systems provide a greater range of motion and finer control, allowing for more precise movements and tasks.
- Power Usage: Electric power systems are more compact and generate less heat, improving the robot's operational longevity and reliability.
woah its flexible!
Benefits of the Electric Model:
| Feature | Hydraulic Atlas | Electric Atlas |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher energy consumption | Lower energy consumption |
| Range of Motion | Limited by hydraulic constraints | Greater flexibility and precision |
| Power Usage | Generates significant heat | Reduced heat generation |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent maintenance | Lower maintenance needs |
| Operational Noise | Louder due to hydraulic systems | Quieter operation |
New Features:
The electric Atlas introduces several new capabilities that enhance its functionality and application potential:
- Three-Fingered Grippers: These grippers provide improved dexterity, enabling Atlas to handle a variety of objects with greater precision and control.
- Improved Control Policies: Advanced control algorithms have been integrated to enhance Atlas's stability and responsiveness during dynamic tasks.
- Enhanced Mobility: The electric actuators allow for smoother and more natural movements, making Atlas more agile and versatile.
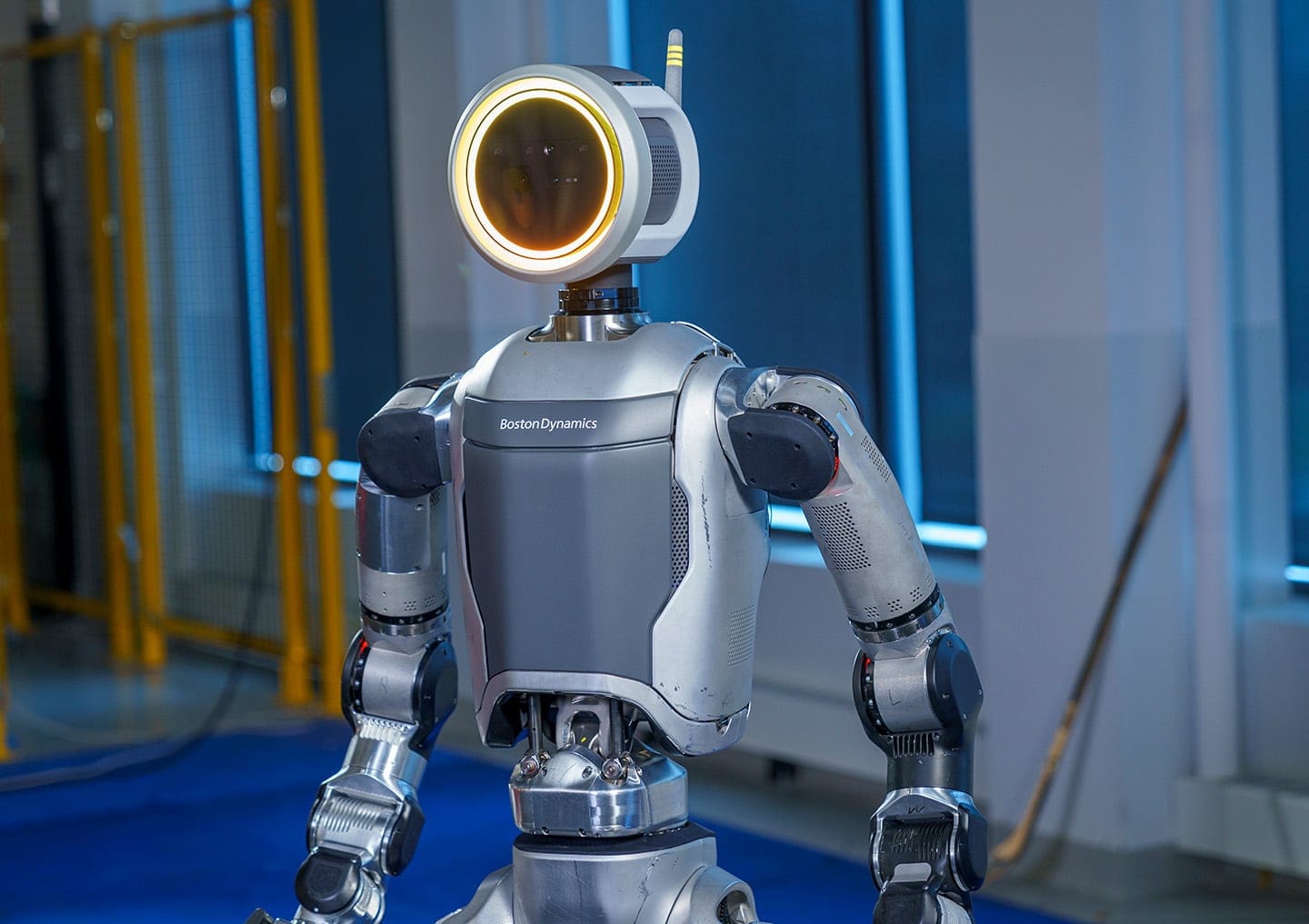

Integration with AI:
The integration of advanced AI technologies plays a crucial role in enhancing Atlas's capabilities:
- Dexterity: AI algorithms enable Atlas to perform complex manipulation tasks that require fine motor skills, such as handling tools and assembling components.
- Autonomy: The AI systems allow Atlas to operate with a higher degree of autonomy, reducing the need for constant human supervision. This includes capabilities like obstacle avoidance, path planning, and real-time decision-making.
- Learning: Machine learning techniques help Atlas adapt to new tasks and environments, continuously improving its performance through experience.
Summary of Technological Advancements:
| Technological Aspect | Hydraulic Atlas | Electric Atlas |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydraulic | Electric |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Range of Motion | Limited | Extensive |
| Dexterity | Basic gripping capabilities | Three-fingered grippers |
| AI Integration | Limited | Advanced AI for dexterity and autonomy |
| Operational Noise | High | Low |
| Maintenance | High | Low |
By embracing electric power and integrating advanced AI, Boston Dynamics has not only improved Atlas's efficiency and dexterity but also expanded its potential applications.

Commercialization and Industry Impact
Unlike its hydraulic predecessor, the electric Atlas offers greater efficiency, reduced operational noise, and lower maintenance requirements, which are critical factors for industrial use.
Industrial Applications:
The electric Atlas is ideal for tasks such as material handling, precision assembly, and inspection in manufacturing settings. Its advanced dexterity and mobility allow it to perform complex tasks that were previously challenging for robots.
Comparison with Spot and Stretch:
While Spot is optimized for inspection and surveillance in facilities, and Stretch is designed for unloading trucks and warehouse automation, Atlas brings a new dimension to Boston Dynamics' portfolio. Atlas's humanoid form and advanced manipulation capabilities make it suitable for tasks that require a higher degree of dexterity and human-like interaction.
Market Potential:
The market readiness for the new electric Atlas is promising, with potential applications spanning various sectors:
- Manufacturing: Atlas can be used for precision tasks, reducing the need for human workers in dangerous or repetitive jobs.
- Healthcare: With its advanced manipulation capabilities, Atlas could assist in surgery, rehabilitation, and patient care.
- Construction: Atlas’s ability to handle tools and navigate complex environments makes it valuable for construction tasks.
- Logistics: The robot can streamline operations in warehouses by handling goods and performing inspections.
Lessons Learned from Spot and Stretch: Building a Better Atlas
Boston Dynamics wasn't new to the humanoid robotics game when they unveiled the latest Atlas. They'd already achieved commercial success with their quadruped robot, Spot, and the warehouse robot, Stretch. These earlier ventures provided valuable insights that undoubtedly shaped the development of the new Atlas.
From Spot to Atlas: Refining Mobility and Agility
Spot's impressive balance and maneuverability likely informed Atlas' own advancements. The latest Atlas boasts superior athleticism and can navigate complex terrain with newfound grace. Lessons learned from Spot's dynamic control systems likely contributed to Atlas' ability to perform parkour flips and even backflips – feats that were unimaginable for previous iterations.


check out more on spot!
Stretch's Influence: Building for Real-World Tasks
Stretch, designed for warehouse logistics, offered valuable lessons in building robots for practical applications. The focus on functionality and user-friendliness in Stretch seems to have carried over to the new Atlas. Its modular design suggests the possibility of customizing Atlas for specific tasks, making it a more versatile tool in various industries.
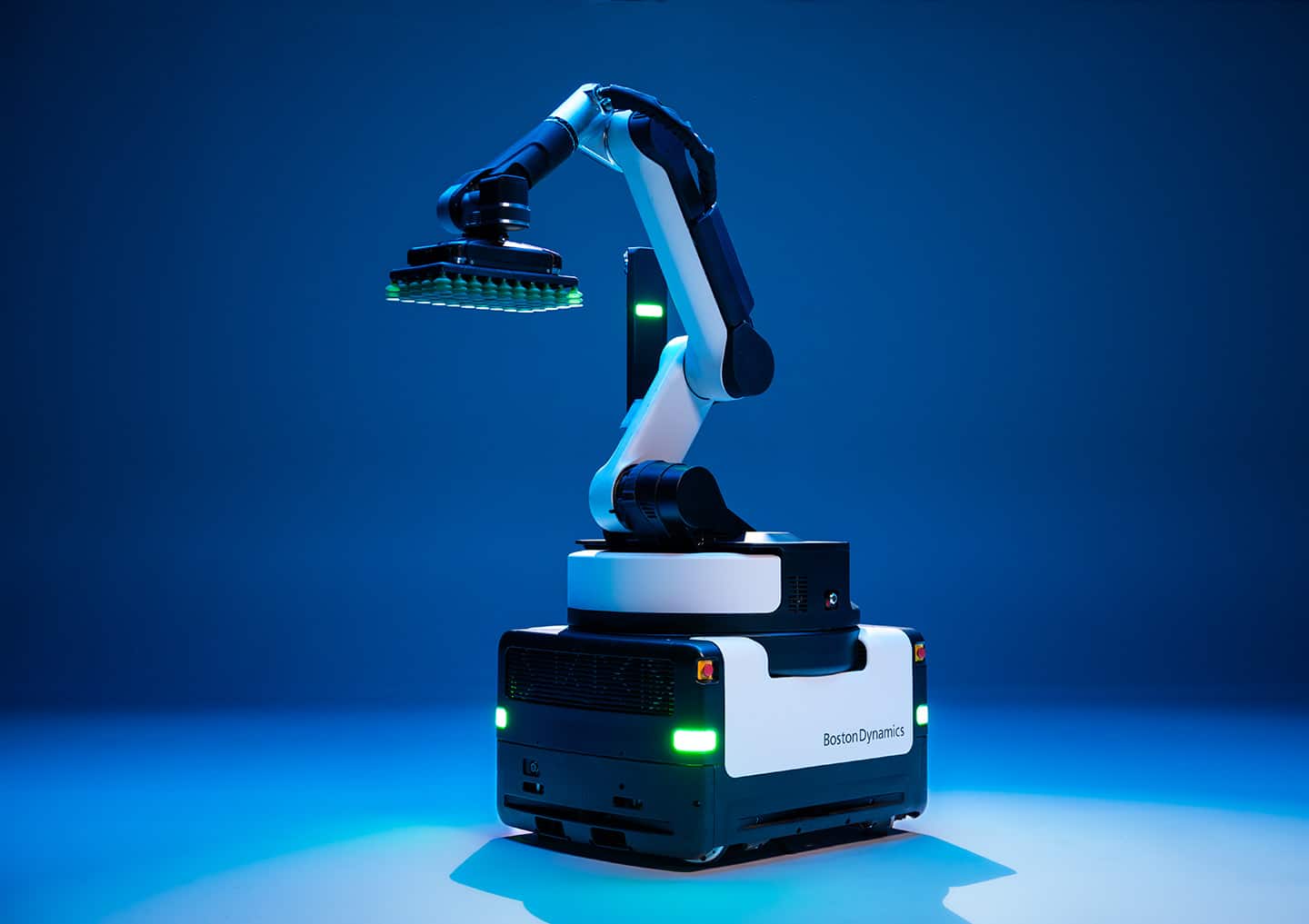

By incorporating the lessons learned from Spot and Stretch, Boston Dynamics seems to have built a more robust, adaptable, and potentially collaborative Atlas. This new generation robot paves the way for a future where robots seamlessly integrate into our workplaces and potentially even our homes.
Safety and Autonomy Considerations
When it comes to legged robots like Atlas, safety is paramount. Boston Dynamics has been at the forefront of developing and adhering to rigorous safety standards to ensure that their robots can operate safely around humans and in dynamic environments. This involves implementing advanced sensors and algorithms to detect and respond to potential hazards.
- Importance of Safety Standards: Boston Dynamics collaborates with organizations like ASTM International to develop safety standards for legged robots. These standards ensure that robots like Atlas can operate safely in various environments, including workplaces and public spaces.
- Boston Dynamics’ Approach: The company integrates multiple safety features, such as real-time 3D vision systems and robust remote operation capabilities, to enhance the safe operation of Atlas.

Path to Autonomy:
Achieving full autonomy in humanoid robots is a complex journey. Boston Dynamics employs use tele-operation as an essential intermediate step, allowing operators to remotely control the robot while gradually improving its autonomous capabilities.
- Teleoperation as a Stepping Stone: Initially, Atlas can be tele-operated to perform tasks, providing valuable data and learning opportunities for improving AI algorithms.
- Higher Levels of Autonomy: As AI systems evolve, Atlas can take on more complex tasks with minimal human intervention. For instance, it can autonomously navigate obstacles, recognize objects, and perform precision tasks.
Examples of Autonomous Operation:
| Task | Teleoperation | Higher Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Navigating Obstacles | Operator controls movements | Atlas uses AI to find optimal paths |
| Handling Objects | Manual control of grippers | Autonomous object recognition and manipulation |
| Inspection Tasks | Guided by operator | Self-directed inspection routines |
Long-Term Prospects:
The future capabilities of Atlas are vast, with potential applications expanding as the technology matures. Boston Dynamics is committed to pushing the boundaries of what humanoid robots can achieve.
Expectations include improved dexterity, increased load capacity, and enhanced AI-driven autonomy. Atlas could revolutionize industries such as healthcare, construction, and disaster response by taking on tasks that are dangerous or impractical for humans.
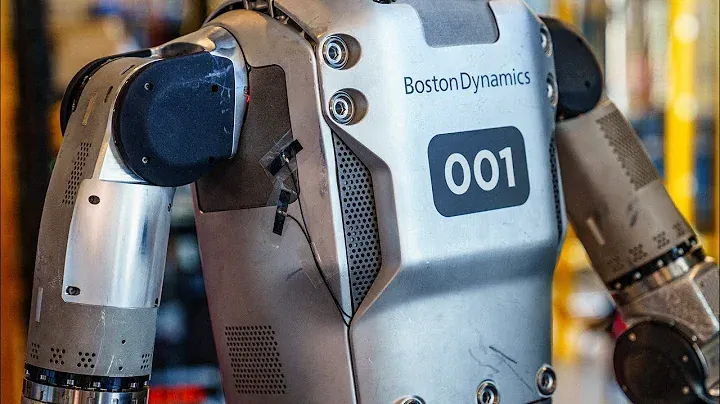

Atlas isn’t just a step forward in robotics; it’s a giant leap towards a future where robots and humans work hand in hand.
As it moves from a research project to a commercial product, Atlas embodies the potential for humanoid robots to transform industries and enhance human capabilities. Its development is a testament to the innovative spirit of Boston Dynamics and their vision of a world where robots play an integral role in our daily lives.
So...are you ready to welcome your own robot companion into your life? The future is here, and it's looking more fascinating (and helpful) than ever! 💪🤖- Giada






![From Tesla to BMW, humanoids are on their way [to your] home](/content/images/size/w300/2024/02/top_humanoids.png)
