The global robotics industry stands at the precipice of a revolution, poised to reshape economies and societies worldwide. While the United States held the initial torch, China has emerged as a dominant force, rapidly deploying robots in its manufacturing sector and nurturing a burgeoning domestic robotics industry. This begs a critical question: can China evolve from a mere imitator to a genuine leader in robotics innovation?

This article explores into the complexities of China's robotics ecosystem, dissecting its strengths, weaknesses, and ambitions. We'll explore the factors propelling its rapid rise, assess its current level of innovation, and examine the potential ramifications for the global robotics landscape.
China's Robotics Boom: Scale and Adoption
China's ascent in robotics has been nothing short of phenomenal. It boasts the world's largest industrial robot market, accounting for a staggering 52% of global installations in 2022. This translates to a robot density of 392 units per 10,000 manufacturing workers, surpassing the United States' 285. However, when adjusted for wage levels, China's robot adoption rate is a remarkable 12.5 times higher than expected, highlighting the government's deliberate push for automation.
Several factors contribute to this remarkable boom:
- Government Support: Robotics has been designated a strategic priority by the Chinese government, with generous subsidies, tax breaks, and research funding fueling both robot adoption and domestic production.
- Rising Labor Costs: As wages in China increase, robots become more cost-competitive, prompting manufacturers to automate tasks previously performed by humans.
- Vast Manufacturing Base: China's colossal manufacturing sector provides a fertile ground for robotics companies, allowing them to achieve economies of scale and reduce costs.
- Shifting Value Chain: China's ambition to ascend the value chain necessitates advanced manufacturing capabilities, with robotics playing a pivotal role in achieving this goal.
This rapid adoption equips Chinese robotics companies with invaluable experience and data, accelerating their growth and development.
Innovation Landscape: Strengths and Weaknesses
While China excels in robot deployment, its innovative capacity remains a subject of debate. Currently, many Chinese robotics companies operate as "fast followers," adept at replicating and adapting existing technologies. However, they often lag behind Western counterparts in terms of groundbreaking innovation and quality. This is evident in China's reliance on imported components and software, particularly for high-end robots.
Blackwell, will be “the engine to power this new industrial revolution – Jensen H. NVidia
However, dismissing China solely as an imitator would be a grave mistake. Several factors point to its burgeoning innovative potential:
- Increased R&D Spending: Chinese robotics companies are rapidly ramping up their R&D expenditures, with some exceeding the R&D intensity of established Western players.
- Research Hubs and Institutes: China has established numerous robotics research institutes and innovation hubs, fostering collaboration between academia and industry.
- Talent Pool: China graduates a significant number of engineers and scientists annually, creating a substantial talent pool for the robotics industry.
- Cutting-Edge Exploration: Chinese companies are actively venturing into pioneering areas like humanoid robots and AI-powered robotics, demonstrating their ambition to push boundaries.
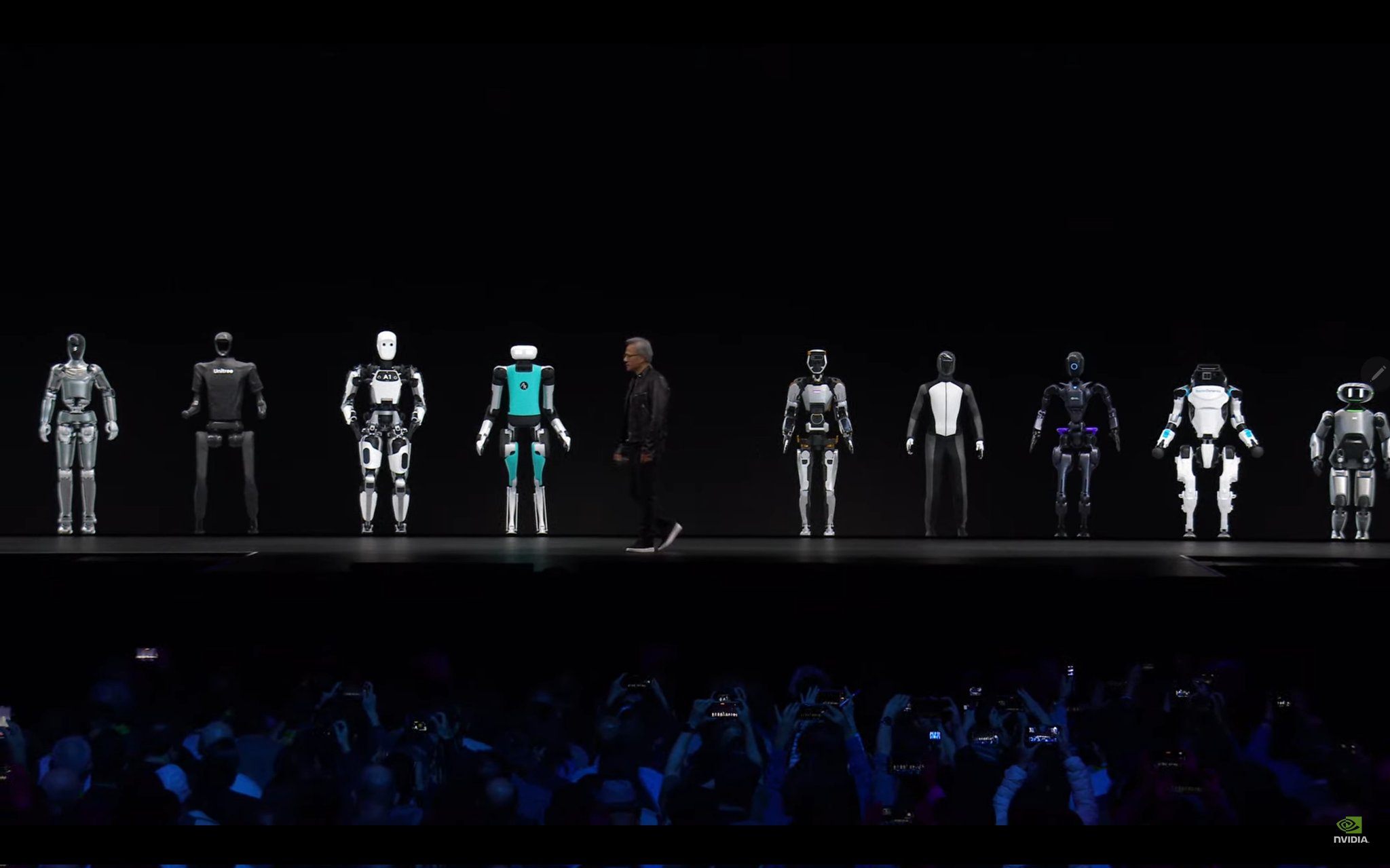

Furthermore, China's success in other technology sectors, such as drones and smartphones, underscores its potential to transition from a fast follower to an innovation leader.
The sheer scale of its domestic market and government support allows Chinese companies to iterate rapidly and refine existing technologies, ultimately leading to the development of unique innovations.

Case Studies: Chinese Robotics Companies in Focus
A closer look at specific companies reveals the diverse landscape of China's robotics industry:
- Ecovacs: A leading manufacturer of robotic vacuum cleaners, Ecovacs invests heavily in R&D and boasts a global presence. While its international market share remains modest, its products have garnered international innovation awards. (Amazon roomba deal anyone?!)
- Roborock: Backed by tech giant Xiaomi, Roborock focuses on intelligent cleaning robots. Its products have captured significant market share and garnered praise for their innovative features.
- Estun: This company has evolved from CNC systems to become a major player in industrial robots. Estun aggressively acquires foreign companies to gain technological prowess and invests heavily in R&D.
- SIASUN: Affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, SIASUN specializes in industrial and mobile robots, as well as intelligent manufacturing solutions. It boasts a large R&D team and is expanding its global footprint.
These examples showcase the varying degrees of innovation within China's robotics industry. While some companies primarily focus on cost-competitiveness, others are actively pursuing cutting-edge technologies and establishing themselves as innovators.

The Ethical Considerations of China's Rise in Robotics
While the economic and technological implications of China's robotics boom are significant, it's crucial to address the ethical considerations that accompany this rapid advancement. Here are some key areas to ponder:
- Job displacement: As automation becomes more widespread, concerns regarding large-scale job losses in manufacturing and other sectors will intensify. Governments and industries must work together to create retraining programs and safety nets for displaced workers.
- Labor practices in robot production: Ethical sourcing of materials and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the robot supply chain are critical. This necessitates international cooperation and robust regulatory frameworks.
- The rise of "algorithmic bias": As robots become more sophisticated and take on decision-making roles, the potential for bias embedded in their algorithms becomes a concern. Efforts to ensure fairness and transparency in robot programming are essential.
- The weaponization of robots: The potential for autonomous weapons systems raises serious ethical and legal questions. International treaties and regulations are needed to prevent an arms race in this domain.
- The impact on human well-being: The increasing presence of robots in society necessitates careful consideration of the psychological and social implications. The focus should be on robots augmenting human capabilities, not replacing human connection.
New video from @1x_tech.
— Tesla Bot Journal (@TeslaBotJournal) March 19, 2024
EVE robot is shown handling a diverse set of objects including deformable items. It can fold a shirt, wipe a table, and also fold the flaps of the cardboard box.
All that is achieved using end-to-end NNs and with two-finger grippers. pic.twitter.com/OTM5lniFOl
Those are all subjects that are very common when it comes to AI and "the old way" of doing business, there's no question that can be answered today because AI will touch every aspect of what we have been taking as norm in every aspect of our society. Sets of labor laws will be questioned within the decade. China has historically not highly focused on the human element when it comes to manufacturing. There's also a cultural acceptance that will make China an incredible playground at global level on this very matter.
The Need for a Global Dialogue
Addressing these complex ethical issues requires a global dialogue involving governments, corporations, ethicists, and technologists. Collaborative efforts are needed to establish international standards and best practices for the responsible development and deployment of robotics.
By proactively tackling these ethical considerations, we can ensure that China's rise in robotics contributes to a future that benefits all of humanity.
This addition emphasizes the ethical considerations surrounding China's advancements in robotics, urging a global discussion to ensure responsible development and deployment of this technology.





